Tajikistan experienced a 4.6 magnitude earthquake at a depth of 80 km in the Pamir Mountain range, marking the eighth such event in 30 days. The region is known for its seismic activity, with 73.7% of its population living in high-magnitude zones. The World Bank highlights the necessity for improved disaster preparedness due to the risks associated with earthquakes.
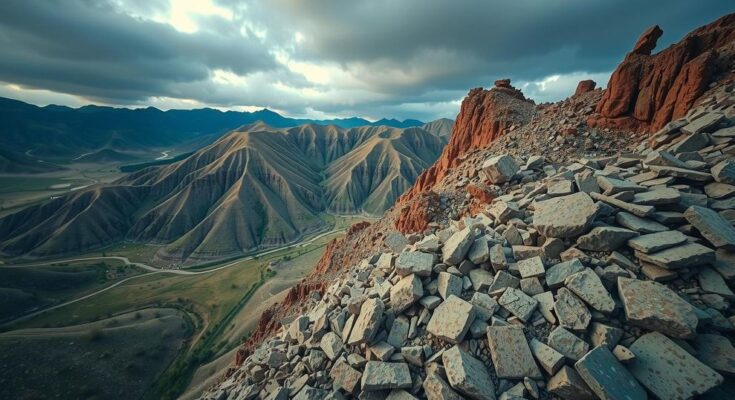
On a recent occasion, Tajikistan was struck by an earthquake measuring 4.6 in magnitude. The seismic event occurred at a considerable depth of 80 kilometers, specifically in the Pamir Mountain range, close to the notable Garam Chashma hot springs. The quake’s coordinates were reported as latitude 37.21 N and longitude 71.49 E by the National Centre of Seismology (NCS). Notably, this event marked the eighth earthquake to impact Tajikistan within a 30-day span.
Tajikistan is situated within a seismically active region. As indicated by previous reports from the World Bank, approximately 50 percent of its territory is classified within the seismic zone capable of producing earthquakes of magnitude 9. Moreover, a significant majority of the population, approximately 73.7 percent of the 8 million residents, resides in areas prone to earthquakes of magnitude 8 or higher. The report emphasized that over recent years, Tajikistan has experienced multiple earthquakes that have resulted in substantial human casualties and extensive material damages.
The World Bank has consistently highlighted the dangers posed by seismic activity in Tajikistan, noting that the entire territory is fundamentally vulnerable to such natural disasters. The consistent occurrence of earthquakes, as evidenced by recent events, poses ongoing risks to both the population and the economy of the nation.
In light of these findings, improvements in earthquake preparedness, response strategies, and infrastructure resilience are necessary to safeguard the people and property of Tajikistan against future seismic events.
The geographical region of Tajikistan is notably characterized by its seismic activity, primarily due to its location in the Pamir Mountain range. Historical data suggests that this area has a long history of earthquakes, significantly impacting communities and infrastructure. The seismology reports highlight a critical need for awareness and preparedness strategies amid these frequent seismic events. The high percentage of the population residing in high-magnitude seismic zones further underscores the urgency of this matter, as the country continues to face the economic ramifications of natural disasters.
In conclusion, the recent earthquake in Tajikistan underscores the persistent threat of seismic activity in this region. With a significant portion of the population residing in high-magnitude zones and a history of devastating earthquakes, proactive measures are crucial. As emphasized by the World Bank, attention must be directed towards enhancing earthquake response and preparedness to mitigate future impacts on human lives and the economy.
Original Source: m.economictimes.com