This article explores the pivotal roles of global forests, particularly those in Russia, Brazil, Canada, the United States, and China, in fostering biodiversity, addressing climate change, and enhancing ecotourism. It underscores the importance of conservation efforts as these forests face threats from deforestation and climate variability, while also highlighting how sustainable travel practices can aid in preserving these invaluable ecosystems.
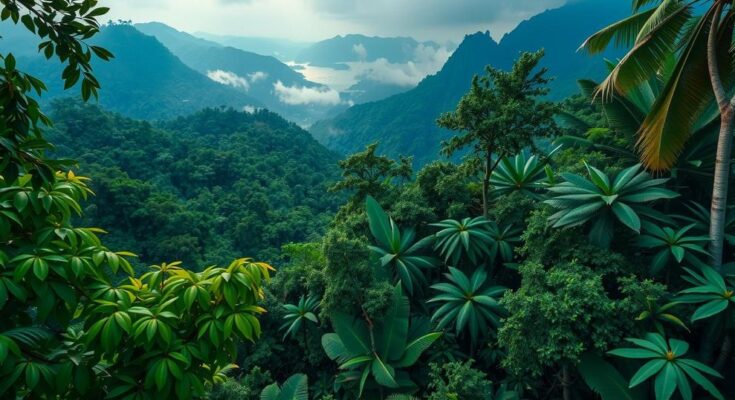
The world’s forests play a critical role in sustaining biodiversity, regulating climate, and sequestering carbon. According to the 2024 UN Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) forest resources assessment, certain nations significantly influence global forest cover, with Russia leading as the country boasting the largest forest area. The boreal forests of Russia, or Taiga, cover over 20% of the world’s forests, providing essential habitats and being vital in the carbon cycle due to their vast carbon storage capacity. In contrast, Brazil’s Amazon rainforest is renowned as a biodiversity epicenter, encompassing nearly 60% of the country’s total forested area. Despite its ecological significance, it is under threat from deforestation driven by agriculture and logging, presenting global conservation challenges. The Amazon’s ability to absorb carbon dioxide underscores its importance in climate regulation, and its degradation poses risks to ecological balance. Canada’s boreal forests, covering about 9% of global forests, exemplify the nation’s dedication to environmental conservation, housing diverse wildlife and serving as a carbon sink essential for climate stability. In the United States, a variety of forest types span across regions, but they face dangers such as wildfires, particularly in California, necessitating robust conservation efforts. China has made strides in reforesting and combating desertification, creating forests that are critical for protecting endangered species and enhancing biodiversity. Many other countries also contribute significantly to global forest preservation and biodiversity. The engagement of the travel industry in ecotourism is rising, as areas with rich forest ecosystems attract tourists seeking adventure and cultural experiences. Nevertheless, it is essential to ensure these regions are safeguarded from the adverse effects of over-tourism, thus emphasizing sustainable practices.
Forests are crucial for maintaining the planet’s ecological equilibrium, significantly contributing to biodiversity and climate health. The 2024 FAO forest resources assessment reveals the dominant role played by countries like Russia, Brazil, and Canada in the global forest landscape. Understanding the contribution of these nations to forest preservation highlights the urgent need for conservation strategies in the face of climate change and biodiversity loss. This context sets the stage for recognizing the interconnectedness of sustainable travel, forest conservation, and global ecological wellbeing.
In conclusion, the world’s forests, particularly those in Russia, Brazil, Canada, the United States, and China, serve as vital elements in maintaining biodiversity and combating climate change. Their ecological significance cannot be overstated, as they not only provide essential habitats for countless species but also play a critical role in carbon sequestration. The travel industry’s growing focus on sustainable tourism further underscores the necessity of protecting these vital ecosystems for future generations.
Original Source: www.travelandtourworld.com