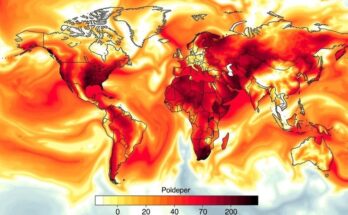
Africa is significantly impacted by climate change despite contributing only 4% of global greenhouse gas emissions. A report by the World Meteorological Organization indicates that extreme weather events, particularly severe flooding, are becoming more frequent due to disrupted weather patterns across the continent.
A recent report from the World Meteorological Organization highlights the severe impact of climate change on Africa, a continent that, despite only contributing about 4% to global greenhouse gas emissions, is experiencing catastrophic extreme weather events. Experts attribute these phenomena to significant disruptions in established weather patterns, leading to intensified flooding and other extreme climate conditions across vast regions of the continent. The report underscores the urgent need for both global recognition of Africa’s plight and immediate action to address the consequences of climate change in these nations.
The phenomenon of climate change has emerged as a critical global issue with far-reaching implications. It is scientifically established that human activities, particularly the combustion of fossil fuels, have led to increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, resulting in a rise in global temperatures. While Africa’s contribution to these emissions is minimal in comparison to industrialized regions, the continent remains disproportionately affected by the consequences of climate change. Extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and erratic rainfall patterns have become more frequent and severe, entirely disrupting the livelihoods of millions in African countries.
In conclusion, while Africa’s contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions is remarkably low, the continent is facing dire challenges due to climate change-induced extreme weather events. With flooding and other natural disasters becoming increasingly severe, it is imperative for the international community to acknowledge and respond to Africa’s pressing climate needs. Continued advocacy for sustainable practices and equitable global resource distribution will be crucial in mitigating the consequences of climate change on vulnerable populations in Africa.
Original Source: www.wionews.com